Ultrasounds and pregnancy - why and why a pregnant woman needs to have a sonography
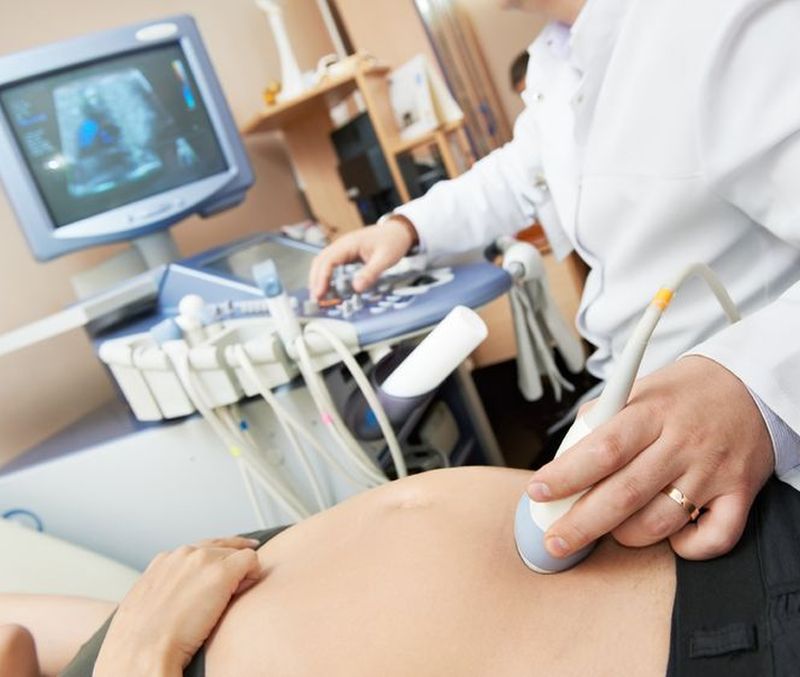
Recommended ultrasounds throughout pregnancy are the only imaging methods that can track the evolution and development of the fetus, placenta and amniotic fluid without adverse effects, and can be repeated as often as needed without the need for training . Throughout the pregnancy, it is recommended that at least four ultrasounds be made, the number of them still varying from patient to patient, depending on the health of the mother and fetus: first, confirmation of the pregnancy, and the next three for each pregnancy trimester. First Trimester Ultrasound The first trimester ultrasound can be performed both transvaginal and transborder. It is intended to fix the embryo in the uterus, as well as the number of girls, approximate the age of pregnancy and, very importantly, assess the nucal translucency, a test that can reveal whether the fetus is at risk of Down syndrome or other diseases caused by chromosomal abnormalities. The second trimester ultrasound - the most important 2nd-trimester Morphometric Ultrasound, is done in the 22nd-24th weeks and allows assessment of the development of the baby and its organs: heart, liver, kidney, head, column, pelvis and limbs. It is the most important ultrasound during the nine months of pregnancy, being one of the most minute ultrasounds (it can last up to 45 minutes).
The third trimester ultrasound takes place around 32-34 weeks in the last trimester of pregnancy, and allows the head to be measured, the length, the fetal growth, the position of the uterus in the uterus, the umbilical cord and the placenta . Other ultrasounds Another ultrasound that is done during pregnancy is Doppler. This is done twice with morphologies of the first and second trimesters to detect heart rhythm pulses and to detect and observe blood flows that pass through the fetal blood vessels. It is the ultrasound recommended especially in high-risk pregnancies, in pregnant women with hypertension, in those at risk of abortion, or in low amniotic fluid. Using the ultrasounds it uses, the ultrasound transposes the fetal image on the screen of the fetus, with possible problems and abnormalities.
This can be done with 2D, 3D or 4D probes. The most commonly used are 2D ultrasounds, which ensure fetal monitoring throughout the pregnancy. With her one can hear the first beating of the heart, but also the first image with it, can estimate the gestational age, the approximate date of birth and, at the right time, can also tell which is the sex of the baby (starting with the 16th week of pregnancy). The procedure takes about half an hour, it does not radiate either the mother or the fetus and presents no risk. In a second ultrasound, somewhere around 12-13 weeks, it is possible to see with this type of ultrasound the brain and bone marrow development and if there are problems in developing the fetus.
The more advanced 3D and 4D ultrasounds provide more real-life images of the fetus, with even the smallest details of its structure and development. I can evaluate, as in the case of 2D ultrasound, the state of health and possible congenital malformations of the fetus. If the 3D ultrasound offers a fetal picture, the 4D gives a three-dimensional image of it, showing the baby's movements in real time. .
Source : csid.ro
Views : 2931
Popular Article
- (photo) Nude becomes art.
Posted: 2018-03-17, 9589 views.
- The harmful effects of air conditioning on the skin
Posted: 2017-06-08, 8269 views.
- 3 causes of dyed hair discoloration
Posted: 2017-06-15, 8142 views.
- Why early puberty occurs in girls: symptoms, favors, diagnosis and treatment
Posted: 2017-10-24, 7999 views.
- Good or bad skin treatments in the hot season
Posted: 2017-06-07, 7737 views.
Recommendations
- (photo) Nude becomes art.
Posted: 2018-03-17, 9589 views.
- The harmful effects of air conditioning on the skin
Posted: 2017-06-08, 8269 views.
- 3 causes of dyed hair discoloration
Posted: 2017-06-15, 8142 views.
- Good or bad skin treatments in the hot season
Posted: 2017-06-07, 7737 views.
- Risks of practicing sports on hot days
Posted: 2017-06-12, 7330 views.
 4 effective ingredients in the fight against acne.
4 effective ingredients in the fight against acne. How to get rid of hiccups fast
How to get rid of hiccups fast The wheat bran diet: the secret of lost pounds as if by magic
The wheat bran diet: the secret of lost pounds as if by magic The recipe that will sweeten your soul this weekend!
The recipe that will sweeten your soul this weekend!  Is it dangerous or not to refreeze meat after thawing it?
Is it dangerous or not to refreeze meat after thawing it?  The unusual sign of diabetes indicated by saliva.
The unusual sign of diabetes indicated by saliva. What to drink to boost your immune system.
What to drink to boost your immune system. 10 foods that help you never age.
10 foods that help you never age. What actually happens in your body if you drink a cup of coffee for breakfast
What actually happens in your body if you drink a cup of coffee for breakfast 5 surprising benefits of chia seeds
5 surprising benefits of chia seeds