Shock waves can treat elbow aches, but also other illnesses.
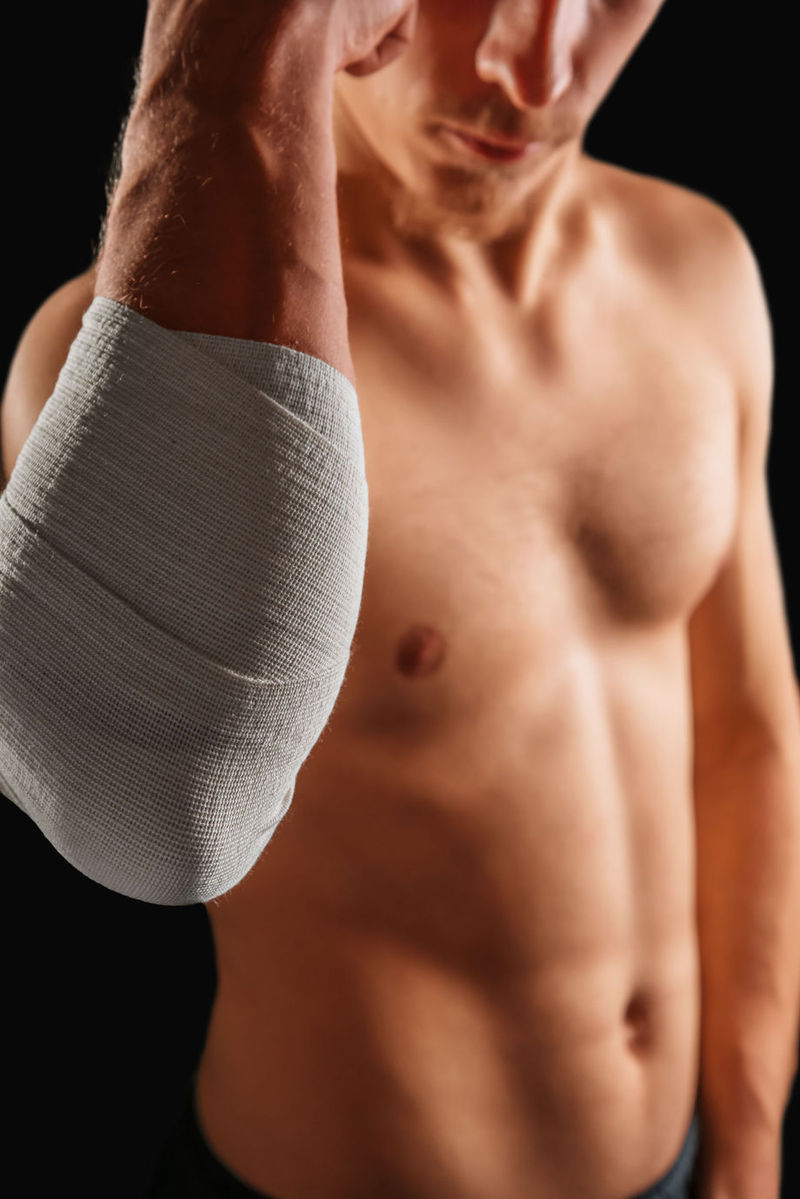
Musculoskeletal pain, caused by chronic conditions or sedentary disease, poorly healed fractures, or sports injuries can be ameliorated over time by shock waves. Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) has begun to be used in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders in Europe in the early 1990s. More specifically, this shock therapy is a derivative of mechanical lithotripsy, ie the procedure of breaking and breaking up kidney stones with sonic waves. Besides, it was also discovered. Following treatment, physicians observed that patients who had other lumbar or musculoskeletal disorders were relieved of pain. Following the studies, it was discovered that the device that emit shock waves calms the spasm, the cause of the pain, Antonia Onaca, medical physician at the Bio-Medica clinic.
How do shock waves work? . Shockwave therapy has the effect of improving metabolism and microleaving, decalcifying fibroblasts, improving collagen production, relieving muscles and rapidly eliminating substance P. The device has been designed for long-lasting research, technology proving its effectiveness especially in the treatment of severe shoulder pain, calcaneal pain, or treatment of elbow pain. Currently, therapy is used successfully and at minimal risk in treating a broad spectrum of skeletal and muscular disorders - plantar fasciitis, epicondylitis, tendinitis and fracture ossification - being preferred to invasive surgery. Patients treated with shock waves recover and return to day-to-day activities within two days.
As effective as surgery for unsaved fractures When fractured bones can not heal, some serious complications may occur, one of which is that the bones are not welded. This happens when the bone healing process is interrupted or stagnated. According to a study conducted in 2009 and published in the Journal of General and Bone Surgery, some cases of non-welding bones have responded well to shock wave therapy, which has been compared by researchers at the level of effectiveness with surgery. The study demonstrates that this appears to result in a metabolic reaction similar to that occurring in the bone during the natural healing process. The microarhitecture of the bone is sensitive to shock waves, indicating that therapy can also be used successfully in the treatment of osteoporosis and osteopathy, Antonia Onaca.
Therapy also helps athletes To reach the superficial and deep structures of soft tissues, as is the case with sports injuries, two types of devices plus paddles are usually needed. That's why another device has been invented that uses shock waves and provides a continuous flow of energy to reach the deepest areas of the tissue without the need for the paddles. The device allows muscles and fascia to be stimulated for muscle problems, ligament problems, and tendon problems, even after acute injuries or after surgery. Recovery time after injuries or surgery can be significantly reduced by combining this technique with others. Shock wave therapy can accelerate muscle regeneration after training or after the game, and by increasing blood pressure and improving lymph flow, it helps you get back into a short period of time, Among the most common sports injuries that can be treated by shock wave therapy are: ankle sprains, muscle breaks, heel tendencies, muscle spasms, cramps and muscle fever, painful patello-femoral syndrome, plantar fasciitis, tibial pain, .
A session lasts for 5-7 minutes Therapy is painless, lasts a little (about 5-7 minutes) and the sitting is done within 7 days. In general, 3 sessions are required, and in special cases, up to 5, up to 6 sessions can be recommended. Contraindications of shock wave therapy refer to patients with malignancies, blood disorders, patients with a history of treatment with anticoagulants, corticosteroids in the last 6 weeks, thrombosis, pregnancy (lumbar and abdominal). Between applications, we recommend resting the affected area. List of treated conditions Tendon disorders due to overuse or degenerative processes (aging) Acute and chronic back pain (cervical, thoracic, lumbar), shoulder, throat, thigh, knee, arm, forearm, calcaneus, etc.
. .
Source : csid.ro
Views : 2489
Popular Article
- (photo) Nude becomes art.
Posted: 2018-03-17, 9119 views.
- The harmful effects of air conditioning on the skin
Posted: 2017-06-08, 7827 views.
- 3 causes of dyed hair discoloration
Posted: 2017-06-15, 7664 views.
- Why early puberty occurs in girls: symptoms, favors, diagnosis and treatment
Posted: 2017-10-24, 7540 views.
- Good or bad skin treatments in the hot season
Posted: 2017-06-07, 7294 views.
Recommendations
- (photo) Nude becomes art.
Posted: 2018-03-17, 9119 views.
- The harmful effects of air conditioning on the skin
Posted: 2017-06-08, 7827 views.
- 3 causes of dyed hair discoloration
Posted: 2017-06-15, 7664 views.
- Good or bad skin treatments in the hot season
Posted: 2017-06-07, 7294 views.
- Risks of practicing sports on hot days
Posted: 2017-06-12, 6888 views.
 4 effective ingredients in the fight against acne.
4 effective ingredients in the fight against acne. How to get rid of hiccups fast
How to get rid of hiccups fast The wheat bran diet: the secret of lost pounds as if by magic
The wheat bran diet: the secret of lost pounds as if by magic The recipe that will sweeten your soul this weekend!
The recipe that will sweeten your soul this weekend!  Is it dangerous or not to refreeze meat after thawing it?
Is it dangerous or not to refreeze meat after thawing it?  The unusual sign of diabetes indicated by saliva.
The unusual sign of diabetes indicated by saliva. What to drink to boost your immune system.
What to drink to boost your immune system. 10 foods that help you never age.
10 foods that help you never age. What actually happens in your body if you drink a cup of coffee for breakfast
What actually happens in your body if you drink a cup of coffee for breakfast 5 surprising benefits of chia seeds
5 surprising benefits of chia seeds